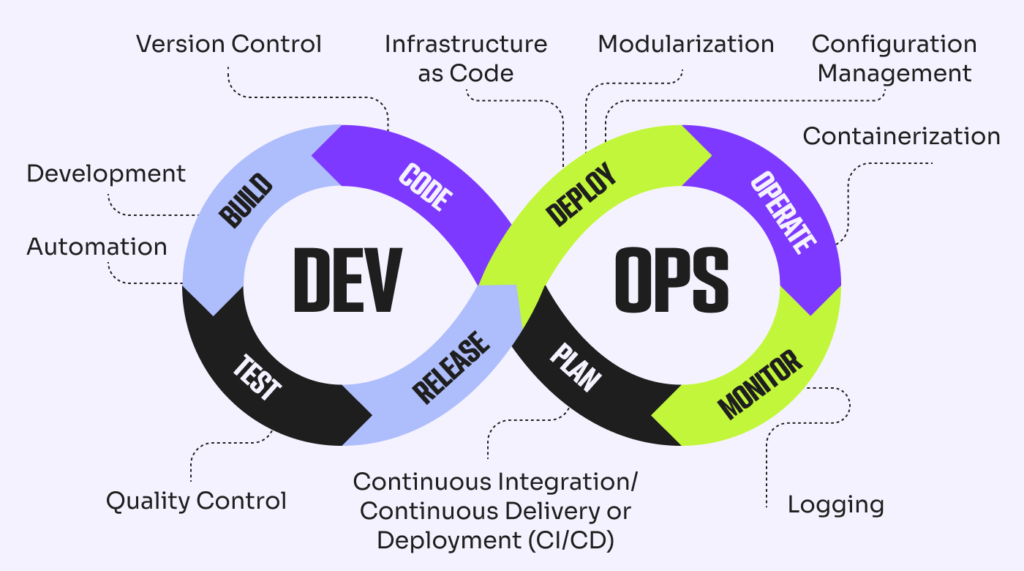
DevOps has become a crucial part of modern software development, offering a set of practices that bridge the gap between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). This integration aims to shorten the development lifecycle while delivering high-quality software continuously. Understanding and implementing DevOps best practices can significantly enhance the efficiency, speed, and reliability of your software delivery processes. This blog delves into the essential DevOps principles, practices, and tools, offering a roadmap for successful implementation.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a culture, movement, or practice that emphasizes the collaboration and communication of both software developers and IT professionals while automating the process of software delivery and infrastructure changes. The goal of DevOps is to establish a culture and environment where building, testing, and releasing software can happen rapidly, frequently, and more reliably.
Key Principles of DevOps
1. Collaboration and Communication: DevOps encourages a culture where development and operations teams work closely together. This collaboration ensures that everyone is on the same page and can work towards common goals.
2. Automation: Automating repetitive tasks such as code integration, testing, and deployment helps in reducing errors, saving time, and ensuring consistency.
3. Continuous Integration (CI): This practice involves frequently integrating code changes into a shared repository. Each integration is verified by an automated build and automated tests to detect errors quickly.
4. Continuous Delivery (CD): Continuous delivery builds on continuous integration by ensuring that code changes are automatically prepared for a release to production. It allows teams to deploy updates and fixes in a reliable and automated way.
5. Infrastructure as Code (IaC): IaC is the practice of managing and provisioning computing infrastructure through machine-readable definition files, rather than through physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools.
6. Monitoring and Logging: Continuous monitoring and logging of applications and infrastructure help in identifying issues in real-time, facilitating prompt responses and ensuring system reliability.
Best Practices for Implementing DevOps
1. Foster a Collaborative Culture
The first step towards implementing DevOps is fostering a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility between development and operations teams. Encourage open communication, regular meetings, and joint planning sessions to ensure alignment on goals and expectations.
2. Automate Everything
Automation is at the heart of DevOps. Automate as many processes as possible, including code integration, testing, deployment, and infrastructure provisioning. This reduces manual errors, saves time, and ensures consistency. Key tools for automation include Jenkins, CircleCI, Travis CI, and Ansible.
3. Implement Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Adopt CI/CD pipelines to automate the process of integrating code changes and deploying them to production. Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI can help set up robust CI/CD pipelines. Ensure that automated tests are in place to validate each integration and deployment.
4. Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Manage your infrastructure using code to ensure consistency and repeatability. Tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, and Ansible allow you to define and manage your infrastructure through code, making it easier to version control and automate infrastructure changes.
5. Monitor and Log Everything
Implement comprehensive monitoring and logging to gain visibility into your applications and infrastructure. Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana), and Splunk can help monitor performance, detect issues, and analyze logs for insights.
6. Embrace Microservices Architecture
Adopting a microservices architecture can enhance the agility and scalability of your applications. Break down monolithic applications into smaller, loosely coupled services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This approach aligns well with the DevOps principles of continuous delivery and automation.
7. Ensure Security with DevSecOps
Integrate security practices into your DevOps workflows by adopting DevSecOps. This involves incorporating security measures throughout the development and deployment processes, ensuring that security is a shared responsibility. Use tools like Snyk, Checkmarx, and OWASP ZAP for continuous security testing.
8. Continuous Improvement and Feedback
DevOps is an iterative process that thrives on continuous improvement. Regularly collect feedback from all stakeholders, including developers, operations, and end-users. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and refine your processes.
Key DevOps Tools
Here are some essential tools that can aid in implementing DevOps best practices:
– Version Control: Git, GitHub, GitLab
– CI/CD: Jenkins, CircleCI, Travis CI, GitLab CI
– Configuration Management: Ansible, Chef, Puppet
– Containerization: Docker, Kubernetes
– Infrastructure as Code: Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, Ansible
– Monitoring and Logging: Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack, Splunk
– Security: Snyk, Checkmarx, OWASP ZAP
Conclusion
Implementing DevOps best practices can transform your software development lifecycle, making it more efficient, reliable, and scalable. By fostering a collaborative culture, automating processes, adopting CI/CD, using infrastructure as code, and continuously monitoring your systems, you can achieve the full potential of DevOps. Embrace these best practices and tools to streamline your development and operations, ultimately delivering high-quality software faster and more efficiently.