Edge computing is rapidly emerging as a transformative technology that promises to revolutionize the way data is processed, analyzed, and acted upon. By bringing computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, edge computing reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and enhances real-time processing capabilities. This blog delves into the rise of edge computing, exploring its benefits, challenges, and potential applications across various industries.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that processes data near the edge of the network, where the data is generated, rather than in centralized data centers or cloud environments. This approach minimizes the distance data must travel, thereby reducing latency and improving speed. Edge computing devices include sensors, IoT devices, gateways, and even local servers that handle data processing tasks locally or at nearby nodes.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers numerous advantages, making it an attractive solution for various applications:
1. Reduced Latency
By processing data closer to the source, edge computing significantly reduces latency. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring systems.
2. Bandwidth Optimization
Transmitting large volumes of data to centralized cloud servers can consume considerable bandwidth and incur high costs. Edge computing mitigates this by processing and filtering data locally, sending only the most relevant information to the cloud. This optimizes bandwidth usage and reduces operational costs.
3. Enhanced Security and Privacy
Edge computing can improve security and privacy by keeping sensitive data closer to its source. By processing data locally, it minimizes the exposure of sensitive information to potential cyber threats that could occur during data transmission to central servers.
4. Improved Reliability
Edge computing enhances the reliability of applications by reducing dependency on centralized data centers. In the event of network outages or disruptions, edge devices can continue to operate and process data locally, ensuring uninterrupted service.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Edge computing enables greater scalability and flexibility by distributing computing resources across multiple locations. This decentralized approach allows for easier expansion and adaptation to changing workloads and requirements.
6. Real-Time Analytics
With edge computing, data can be analyzed in real-time, enabling immediate insights and actions. This is particularly valuable for applications like predictive maintenance, where timely analysis of data can prevent equipment failures and reduce downtime.
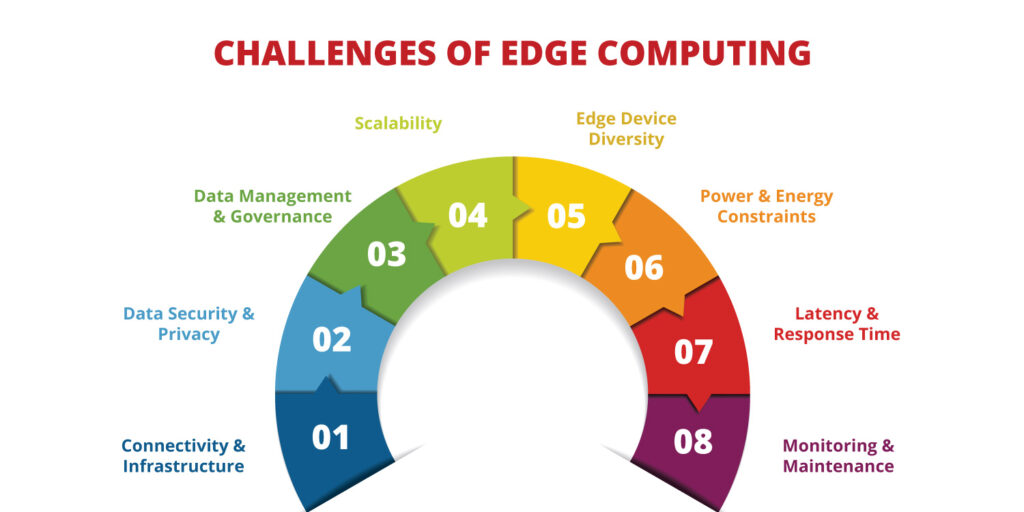
Challenges of Edge Computing
While edge computing offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that must be addressed for successful implementation:
1. Infrastructure Complexity
Deploying and managing edge computing infrastructure can be complex. It involves coordinating numerous distributed devices, ensuring they are properly configured, maintained, and synchronized with central systems. This complexity requires robust management tools and strategies.
2. Security Concerns
While edge computing can enhance security by keeping data local, it also introduces new security challenges. Edge devices can be more vulnerable to physical tampering, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access. Ensuring the security of edge devices and the data they process is paramount.
3. Data Consistency
Maintaining data consistency across distributed edge devices and central systems can be challenging. Synchronizing data, managing updates, and ensuring consistency requires effective data management and synchronization protocols.
4. Limited Processing Power
Edge devices often have limited processing power compared to centralized cloud servers. This can constrain the complexity and scale of tasks that can be performed locally. Balancing the processing load between edge and central systems is essential to optimize performance.
5. Network Dependence
While edge computing reduces reliance on central networks, it still requires robust local network connectivity. Network issues at the edge can impact the performance and reliability of edge applications. Ensuring reliable local network infrastructure is critical.
6. Cost Considerations
Deploying and maintaining edge computing infrastructure can incur significant costs. This includes the costs of edge devices, local servers, network infrastructure, and management tools. A careful cost-benefit analysis is necessary to justify the investment in edge computing.
Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing has a wide range of applications across various industries, driven by its ability to provide real-time processing, enhanced security, and improved reliability:
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing plays a crucial role in autonomous vehicles by enabling real-time data processing for navigation, obstacle detection, and decision-making. Local processing reduces latency, ensuring timely responses to changing driving conditions.
2. Industrial IoT
In industrial settings, edge computing supports real-time monitoring and control of machinery and equipment. Predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization are enhanced by processing data locally, reducing downtime, and improving efficiency.
3. Healthcare
Edge computing enables real-time patient monitoring and diagnostics in healthcare. Wearable devices and local health monitoring systems can analyze data on-site, providing immediate alerts and insights to healthcare providers.
4. Smart Cities
Smart city applications, such as traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety, benefit from edge computing. Processing data locally allows for quicker responses to traffic congestion, pollution levels, and emergency situations.
5. Retail
In retail, edge computing enhances customer experiences through real-time inventory management, personalized marketing, and seamless checkout processes. Local processing enables faster transactions and better customer service.
6. Agriculture
Edge computing supports precision agriculture by enabling real-time monitoring of soil conditions, weather, and crop health. Farmers can make data-driven decisions to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, improving yields and resource efficiency.
7. Telecommunications
Telecommunications providers use edge computing to optimize network performance and deliver low-latency services. Content delivery networks (CDNs) leverage edge computing to cache and distribute content closer to users, enhancing streaming and web performance.
The Future of Edge Computing
The future of edge computing is promising, with several trends and advancements on the horizon:
1. Integration with 5G
The rollout of 5G networks will significantly enhance the capabilities of edge computing. With higher speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity, 5G will enable more sophisticated and real-time edge applications, driving innovation across various sectors.
2. AI at the Edge
The integration of AI and machine learning at the edge will enable more intelligent and autonomous systems. Edge AI can process and analyze data locally, enabling real-time decision-making and adaptive responses in applications such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and smart devices.
3. Edge-to-Cloud Continuum
The development of seamless integration between edge and cloud environments will create a unified computing continuum. This approach will allow for efficient data processing and resource allocation, optimizing performance and scalability.
4. Enhanced Security Measures
Advancements in security technologies and protocols will address the unique challenges of edge computing. Enhanced encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms will ensure the protection of data and devices at the edge.
5. Increased Adoption in Emerging Markets
Edge computing will play a crucial role in bridging the digital divide in emerging markets. By enabling local data processing and reducing dependence on centralized infrastructure, edge computing can enhance connectivity and access to digital services in remote and underserved areas.
Conclusion
Edge computing is poised to transform the landscape of data processing and analysis, offering numerous benefits such as reduced latency, optimized bandwidth, enhanced security, and improved reliability. However, it also presents challenges that must be addressed to realize its full potential. As technology continues to advance, the integration of edge computing with 5G, AI, and cloud environments will drive innovation and unlock new possibilities across various industries. Embracing edge computing can pave the way for smarter, more efficient, and resilient systems, shaping the future of technology and connectivity.